Hippocratic facies
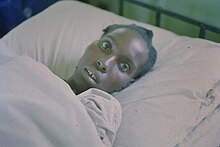
The Hippocratic facies (Latin: facies Hippocratica)[1] is the change produced in the face recognisable as a medical sign known as facies and prognostic of death. It may also be seen as due to long illness, excessive defecation, or excessive hunger, when it can be differentiated from the sign of impending death. (The term typhoid facies refers to the staring expression often seen in typhoid fever).
"[If the patient's facial] appearance may be described thus: the nose sharp, the eyes sunken, the temples fallen in, the ears cold and drawn in and their lobes distorted, the skin of the face hard, stretched and dry, and the colour of the face pale or dusky ... and if there is no improvement within [a prescribed period of time], it must be realized that this sign portends death."[2]
The Hippocratic facies is named after Hippocrates, who first described it.
A related term is cachexia, which is the bodily wasting syndrome often associated with death.
References
[edit]- ^ "Medical Definition of HIPPOCRATIC FACIES". www.merriam-webster.com.
- ^ Chadwick, J. & Mann, W.N.(trans.) (1978). Hippocratic writings. Harmondsworth, UK: Penguin. pp. 170–171. ISBN 0-14-044451-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
