Subregion
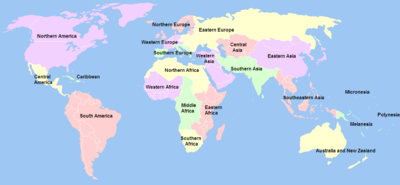
A subregion is a part of a larger geographical region or continent. Cardinal directions are commonly used to define subregions. There are many criteria for creating systems of subregions; this article is focusing on the United Nations geoscheme, which is a changing, constantly updated, UN tool based on specific political geography and demography considerations relevant in UN statistics.
United Nations subregions
[edit]The Statistics Division of the United Nations (UN) is in charge of the collection, processing, and dissemination of statistical information for the UN.[1] In 1999, it developed a system of macro-geographical (continental) regions, subregions, and other selected economic groups to report advances towards achieving numerous millennial development goals worldwide. These statistical divisions were devised for statistical purposes and is used for carrying out statistical analysis.[2] The division's first publication was the book World's Women 2000: Trends and Statistics in 2000.
According to the UN, the assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories.[3]
Subregions by continent
[edit]The following is a non-exhaustive list of subregions, arranged alphabetically by region (i.e., by continent); in the UN geoscheme, higher-level, macro-geographical regions are arranged to the extent possible according to continents.
Sequence used in the list (not all criteria are applied to each continent):
- by the UN Statistics Division's geoscheme
- by geography
- by physiography
- by geopolitics
- by human geography
- by economics
- by culture
- by language
- by religion
- by biogeography
- by historical division
- by geology
Afro-Eurasia
[edit]Afro-Eurasia is a continental landmass comprising the continents of Africa, Asia, and Europe.
- by the United Nations Statistics Division's geoscheme (see also: UN geoscheme for Africa):
- by geography:
- North Africa (Also known as Saharan Africa)
- Maghreb (AKA Northwest Africa, also including Mauritania, which most geographers consider as a part of West Africa; some geographers consider Libya as a part of Northeast Africa and Western Sahara as a part of West Africa)
- Northeast Africa (including Egypt, the Horn of Africa, and the Sudans; some geographers consider Egypt, Libya, and the Sudan as Northeast Africa instead)
- Sub-Saharan Africa (AKA Tropical Africa)
- Central Africa (AKA Congo, Equatorial Africa or Middle Africa)
- East Africa (AKA Nile)
- Northeast Africa (including Egypt, the Horn of Africa, and the Sudans; some geographers consider Egypt, Libya, and the Sudan as Northeast Africa instead)
- Southeast Africa (also including Botswana, Eswatini and Lesotho, which most geographers consider as part of Southern Africa)
- Southern Africa (AKA Kalahari)
- West Africa (AKA Niger)
- North Africa (Also known as Saharan Africa)
- by physiography:
- by economics:
- African Monetary Union (AMU)
- Arab League (including some West Asian countries)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- Common Monetary Area (CMA)
- Community of Sahel–Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Council of Arab Economic Unity (GAFTA) – including some West Asian countries
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- EMEA (including Europe and the Middle East)
- Southern African Customs Union (SACU)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- Union for the Mediterranean (including most Southern European countries and some West Asian countries)
- by biogeography:
- by historical division:
- by geology:
Eurasia is a continental mainland comprising the continents of Asia and Europe.
- by the United Nations Statistics Division's geoscheme (see also: UN geoscheme for Asia):
- Central Asia
- Eastern Asia
- South-eastern Asia
- Southern Asia – the UN geoscheme includes Afghanistan and Iran in this subregion
- Western Asia – the UN geoscheme includes Cyprus, the South Caucasus (Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia), and Turkey in this subregion
- by geography:
- Central Asia
- East Asia
- Greater China
- China
- Hong Kong (some geographers consider it as a part of Northeast Asia)
- Macau (some geographers consider it as a part of Northeast Asia)
- Mainland China (some geographers consider it as a part of Northeast Asia)
- North China (Eastern Inner Mongolia is also a part of Northeast China)
- Northeast China (AKA Manchuria) – also a part of Northeast Asia
- Southeast China (excluding Central China)
- East China (some geographers include Taiwan Island, Penghu, Kinmen, the Matsu Islands, Socotra Rock, Parangcho, and the Senkaku Islands in this subregion)
- South Central China
- Central China
- South China (including Hainan Island and the South China Sea Islands, some geographers also include Hong Kong and Macau in this subregion)
- Western China
- Northwest China (some geographers consider Qinghai and Xinjiang as part of Central Asia)
- Southwest China (some geographers consider Tibet as a part of Central Asia)
- South China Sea Islands (some geographers consider them as part of Northeast Asia)
- Taiwan (some geographers consider it as a part of Northeast Asia)
- China
- Mongolia (some geographers consider it as a part of Central Asia or Northeast Asia)
- Northeast Asia
- China
- Eastern Inner Mongolia
- Northeast China (AKA Manchuria)
- Japan
- Korea
- Russian Far East (also a part of North Asia, but not a part of East Asia)
- China
- Greater China
- North Asia (AKA Siberia)
- Russian Far East (also a part of Northeast Asia)
- South Asia
- Southeast Asia
- West Asia (AKA Southwest Asia)
- Anatolia (AKA Asia Minor)
- Arabia
- Eastern Arabia
- Hejaz (AKA Western Arabia)
- Najd (AKA Central Arabia)
- South Arabia
- Levant
- Mesopotamia
- South Caucasus (AKA Transcaucasia)
- by physiography:
- Anatolian Peninsula
- Arabian Peninsula
- Bahrain Island
- Caucasus Mountains
- Daitō Islands
- Eurasian Steppe
- Fertile Crescent
- Hainan Island
- Himalayas
- Indian subcontinent
- Indochinese Peninsula
- Indo-Gangetic Plain
- Indus Valley
- Iranian Plateau
- Japanese Archipelago
- Jeju Island
- Junggar Basin
- Kolyma
- Korean Peninsula
- Leizhou Peninsula
- Liaodong Peninsula
- Malay Archipelago (including New Guinea)
- Mongolian Plateau
- Nanpō Islands
- Qinghai Lake
- Shandong Peninsula
- Sichuan Basin
- Sri Lanka Island
- Taiwan Island
- Tarim Basin
- by geopolitics:
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) – including Oceania
- Greater Middle East – including some African countries
- Middle East and North Africa (AKA MENA) – including North African countries
- Middle East (AKA the Near East) – including Egypt
- Arab League (AKA the Arab states) – including some African countries
- Mashriq – including Egypt and the Sudan
- Arabian Peninsula
- Levant – including Ash-Shām and Cyprus
- Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq)
- Mashriq – including Egypt and the Sudan
- Asia Minor
- South Caucasus (AKA Transcaucasia)
- Arab League (AKA the Arab states) – including some African countries
- Middle East (AKA the Near East) – including Egypt
- The 'stans
- Middle East and North Africa (AKA MENA) – including North African countries
- Indian subcontinent
- Himalayan states – including China
- Kashmir
- by economics:
- Arab League – including some African countries
- ASEAN Free Trade Area
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue (ACD) – including Russia
- Asian Clearing Union (ACU)
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) – including Oceania
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- Bamboo network
- Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal Initiative (BBIN)
- Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)
- Council of Arab Economic Unity (GAFTA) – including some African countries
- EMEA (including Africa and Europe)
- Eurasian Customs Union (ECU) – including Belarus
- Eurasian Economic Union (EEU) – including Belarus
- Greater Mekong Subregion
- Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)
- South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation (SASEC)
- Union for the Mediterranean (including most Southern European countries and North African countries)
- by culture:
- Eastern world
- Muslim world (AKA the Islamic world)
- Arab world
- Malay world
- Turkic world
- Azerbaijan
- Soviet Central Asia (excluding Tajikistan)
- Turkey
- Xinjiang
- Dzungaria (northern half of Xinjiang)
- Southern Xinjiang
- Greater Iran
- by religion:
- by biogeography:
- by historical division:
- East Indies (AKA the Indies)
- by geology:
- by the United Nations Statistics Division's geoscheme (see also: UN geoscheme for Europe):
- Eastern Europe – the UN geoscheme includes parts of Central Europe (Czechia, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia), parts of South-eastern Europe (Bulgaria and Romania), and Northern Asia (Siberia) in this subregion
- Northern Europe – the UN geoscheme includes the Baltic states, the British Isles, and the Channel Islands in this subregion
- Southern Europe – the UN geoscheme includes Slovenia in this subregion
- Western Europe – the UN geoscheme includes parts of Central Europe (the DACH countries and Liechtenstein) in this subregion
- by geography:
- by physiography:
- by geopolitics:
- by economics:
- Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA)
- Commonwealth of Independent States Free Trade Area (CISFTA) – including Armenia and most Central Asian countries
- Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) – including Canada
- EMEA (including Africa and the Middle East)
- Eurasian Customs Union (EACU) – including Armenia and Kyrgyzstan
- Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) – including Armenia and Kyrgyzstan
- European Economic Area (EEA) – including Cyprus
- European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
- European Single Market (including Cyprus)
- European Union Customs Union (EUCU) – including Cyprus and Turkey
- European Union–Turkey Customs Union (including Cyprus and Turkey)
- Eurozone (including Cyprus)
- North Sea Region (NSR)
- Union for the Mediterranean (UfM) – including some West Asian countries and most North African countries
- Union State
- by culture:
- Balkans
- Baltic states
- Benelux
- Mediterranean Region
- Nordic countries and Karelia
- North Sea Region
- Sápmi, since 1809 divided between Finland and Sweden
- Scandinavia
- Visegrád Group
- by language:
- by religion:
- by biogeography:
- by historical division:
The Americas is a continental landmass comprising the continents of North America and South America.
- by the United Nations Statistics Division's geoscheme (see also: UN geoscheme for the Americas):
- Latin America and the Caribbean
- Caribbean[4] – the UN includes the Lucayan Archipelago in this subregion
- Central America[4] – the UN geoscheme includes Mexico in this subregion
- South America
- Northern America[4]
- Latin America and the Caribbean
- by culture:
- by economics:
- by geography:
- Middle America
- Northern America
- Bermuda
- Canada
- Greenland
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- United States (excluding Hawaii)
- Alaska
- Contiguous United States
- Central United States
- Eastern United States
- Northern United States
- Great Lakes region (including Ontario, Canada)
- Southern United States
- Western United States (including Alaska and Hawaii)
- Northwestern United States
- Southwestern United States (some geographers include the Oklahoma Panhandle and West Texas in this subregion)
- by physiography:
- by geopolitics:
- by economics:
- by culture:
- by biogeography:
- by geography:
- Eastern South America: Federative Republic of Brazil
- Northern South America – the part of South America located in the Northern Hemisphere
- North-eastern South America: The Guianas
- North-western South America: Caribbean South America
- Southern South America: Southern Cone
- Western South America: Andean States
- by physiography:
- by economics:
- by geology:
- by the United Nations Statistics Division's geoscheme:
- by geography:
- Antarctic and Subantarctic islands
- Bouvet Island (some geographers consider it as a part of South America)
- French Southern Territories (excluding Adélie Land and the Scattered Islands)
- Crozet Islands (some geographers consider them as part of Africa)
- Kerguelen Islands (some geographers consider them as part of Africa)
- Saint Paul and Amsterdam Islands (some geographers consider them as part of Africa)
- Heard Island and McDonald Islands (some geographers consider them as part of Oceania)
- Macquarie Island (some geographers consider it as a part of Oceania)
- New Zealand Subantarctic Islands (some geographers consider them as part of Oceania)
- Peter I Island
- Prince Edward Islands (some geographers consider them as part of Africa)
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (some geographers consider them as part of South America)
- South Orkney Islands
- South Shetland Islands
- Mainland Antarctica
- Antarctic and Subantarctic islands
- by the United Nations Statistics Division's geoscheme (see also: UN geoscheme for Oceania):
- Australia and New Zealand – the UN geoscheme includes the Cato, Elizabeth, and Middleton reefs, the Lord Howe Island Group, and Norfolk Island in this subregion
- Melanesia – the UN geoscheme includes New Caledonia and New Guinea in this subregion
- Micronesia
- Polynesia – the UN excludes New Zealand from this subregion
- by geography:
- Australasia
- Australia–New Guinea
- Australia (excluding the Australian Indian Ocean Territories, Heard Island and McDonald Islands and Norfolk Island)
- Ashmore and Cartier Islands
- Coral Sea Islands Territory (excluding the Cato, Elizabeth, and Middleton reefs)
- Mainland Australia
- Tasmania (excluding Macquarie Island)
- New Guinea (some geographers consider it as a part of Melanesia)
- Papua New Guinea (excluding the New Guinea Islands Region)
- Western New Guinea
- Australia (excluding the Australian Indian Ocean Territories, Heard Island and McDonald Islands and Norfolk Island)
- Australian Indian Ocean Territories
- Heard Island and McDonald Islands
- Macquarie Island
- Zealandia
- Cato Reef
- Elizabeth Reef
- Lord Howe Island Group
- Middleton Reef
- New Caledonia (also a part of Melanesia)
- New Zealand (some geographers consider it as a part of Polynesia)
- Norfolk Island
- Australia–New Guinea
- Pacific Islands
- Melanesia (some geographers consider it as a part of Australasia)
- Island Melanesia
- Fiji (excluding Rotuma)
- New Caledonia (also a part of Zealandia)
- New Guinea Islands Region (excluding Bougainville)
- Santa Cruz Islands
- Solomon Islands (archipelago)
- Bougainville
- Solomon Islands (excluding the Santa Cruz Islands)
- Vanuatu
- New Guinea (also a part of Australia–New Guinea)
- Island Melanesia
- Micronesia (some geographers include the Bonin Islands and the Volcano Islands in this subregion)
- Polynesia (some geographers include Clipperton Island in this subregion)
- Melanesia (some geographers consider it as a part of Australasia)
- Australasia
- by human geography:
- by biogeography:
- by geology (see also: Geology of Australia):
See also
[edit]- Autonomous administrative division
- Continent
- Continental fragment
- European Committee of the Regions
- Euroregion
- List of continents and continental subregions by population
- List of Latin names of regions
- Military district
- Polar regions of Earth
- Region
- Regional district
- Regional municipality
- Subcontinent
- Submerged continent
- Supercontinent
- United Nations geoscheme











